Thoracic osteochondrosis is a disease in which the intervertebral discs in the thoracic spine are destroyed. Since this ward is the most inactive, it is less susceptible to the disease.
For thoracic osteochondrosis, spasms and pains in the chest, under the ribs, shortness of breath, stabbing, cutting, sharp pain behind the sternum are characteristic. Symptoms and manifestations of the disease can be similar to other diseases.
Symptoms
Spine pain are the most common and superficial symptoms. Of course, they do not always talk about the development of osteochondrosis in a person. Therefore, you should pay attention to other sensations in the body:
- Discomfort and pain in the chest. Often with a sedentary lifestyle, you may not notice this. But as soon as you start doing any physical activity that speeds up breathing, you will notice that the pain intensifies. The nature of this pain can be called a girdle.
- In addition, you may experience pain in completely unexpected places - the area of the heart, stomach, liver. This is due to the fact that thoracic osteochondrosis tends to "mask" as a particular disease. For example, many may confuse it with gastritis, ulcers, or angina pectoris.
- If you notice that you periodically have "goosebumps" in the chest area, in combination with other manifestations this may indicate thoracic osteochondrosis.
- In some cases, there may be a loss of sexual function, for example, impotence in men.
Pain in thoracic osteochondrosis
One of the main features of this type of pain is the girdle. But it is not always possible to recognize this pain from it. Here is another way it can be felt and characterized:
- most often it manifests itself in the dark, behind the breastbone;
- a sensation that can be described as "a stake in the chest";
- discomfort in the hypochondrium, both right and left;
- feeling as if there is a foreign body behind the breastbone;
- if the lesion touched only the upper part of the thoracic region, pain may be felt by a person in the region of the esophagus and pharynx.
Since these symptoms are still very vague and can indicate a number of other diseases, the doctor recommends an additional ECG test.
Effect on the organs
In the process of development, this disease can negatively impact internal organs, namely the lungs and heart. Here's what thoracic osteochondrosis can entail:
- effect on the heart. Primarily, it causes pinching of the nerve roots in the chest area. After all, that's where the nerve cardiac plexuses start from. It is these plexuses that regulate the work of the heart. The main alarm bells here are regular heart palpitations (extrasystoles), arrhythmia, tachycardia. The effects on the circulatory system, therefore, can manifest themselves in one of these symptoms, or in all of them at the same time;
- effect on the lungs. It most often manifests itself with difficulty in breathing and painful sensations at the same time.
Why does thoracic osteochondrosis appear?
Despite the fact that osteochondrosis as a holistic disease is quite common, thoracic osteochondrosis is less common. The prerequisites for the occurrence of this disease can be found already in schoolchildren who, with a grimace, are sitting at their desks. For this reason, children can develop scoliosis and, at a later age, osteochondrosis. Most of the other causes of development are closely related to scoliosis:
- violation of posture;
- violation of metabolic processes affecting the integrity of the intervertebral discs;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hereditary causes;
- spinal injury;
- static work and prolonged stay in an awkward and twisted posture.
How to treat?
After an accurate diagnosis is established during tests, the doctor prescribes a special drug. In the case of thoracic osteochondrosis, it can include the following drugs, depending on the severity of the disease and the characteristics of its manifestation:
- First of all, drugs are prescribed that "remove" pain and relieve discomfort. They are called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or glucocorticosteroids.
- To avoid a lack of fluid in the intervertebral disc, papain is used.
- Prescribe drugs called "chondroprotectors". With their help, there is a general strengthening of the cartilage tissue.
- Medicines that relieve spasms of the muscles around the spine can be added to the list.
- If the development of the inflammatory process is detected, special anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed.
But, of course, medicines alone cannot be cured. Make sure you follow a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition. These actions will be useful not only for the treatment, but also for the prevention of this and many other diseases.
Exercises for thoracic osteochondrosis
Since the lack of physical activity is one of the fundamental causes of the development of the disease, the role of exercise in this case is great. Also, by supplementing the drug treatment with exercises, your body will return to normal and stabilize much faster.
There are a number of special exercises for the thoracic region. When performing them, follow the basic rules: no jerks, act slowly, smoothly, without trying to overload the body. An increase in amplitude is allowed, but only if no pain is felt. So what are the most effective exercises offered by physical therapy?
- Lie on the floor on your stomach. The hands are along the body. We bend in the thoracic region - softly, gently. Raise your arms and head as high as you feel, but try to avoid the pain. It is recommended to carry out at least 5 approaches.
- For the next exercise, we need a chair with a small, sturdy backrest. We sit up straight in a chair. We exhale, bending backwards, moving our hands back. Then we return to the starting position. We repeat 10-12 times.
- We stand straight. Hands at the seams, legs together. Take a deep breath and raise your hands. As you exhale, slowly lean back and lower your arms. Let's go back to the starting position. It is recommended to do 7-9 sets at a time.
- Get down on all fours. Slowly bend your back as you inhale, as you exhale, return to the starting position. Repeat the exercise 7-10 times.
- We lie on the ground on our stomachs. Hands at the seams. Your task is to tear the body off the floor, stretching the head to the heels. We pull the whole body, train the chest. The required number of approaches is 7-8.
- We work with the upper part of the thoracic region. Starting position: arms at the seams, feet shoulder-width apart. We work with the shoulders. We lift them first together, then each separately. We turn our shoulders forward - back, forward - back. We perform 10-15 approaches for each activity.
- Also, for the upper part of the thoracic region, you can make circular movements with your hands. Starting position, as in the previous activity. Stretch your arms to the sides, clench your palms into fists. We perform the rotation of the fists forward - back, then the rotation of the arm from the elbow - back and forth, then the whole arm back and forth. We perform each part of the exercise 4-6 times, in general we repeat the exercise 2-4 times.
Practice in the morning and evening, giving it at least 15-20 minutes. Dilute it with a series of exercises for other muscle groups by entering some of the options described above.
Massage
Massage is also an excellent tool in the fight against osteochondrosis. Here is a therapeutic massage, which is prescribed by a specialist after a thorough examination of the patient. You can also do it at home - here are some options on how to do it.
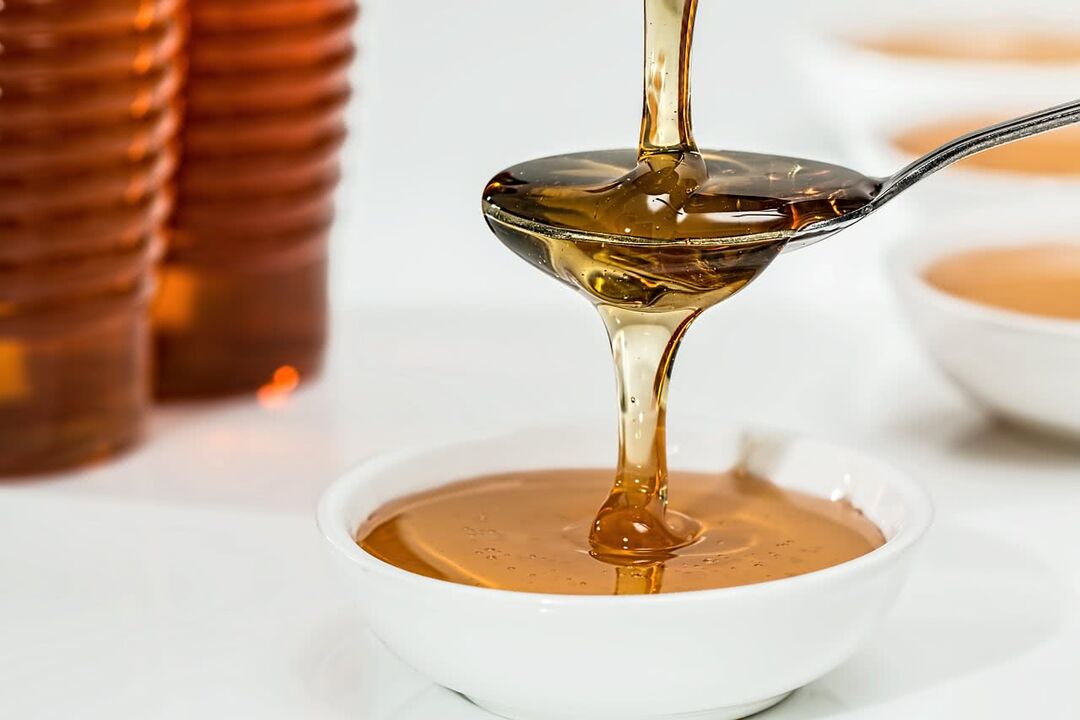

Honey massage. We will need 2-3 tablespoons of honey, preferably not candied, warm. We dip the palms in honey so that they are covered with a thin layer. We apply it to the area behind the sternum and sharply tear it off, repeat several times, moving the palms from place to place.
This massage should not be done for too long, as it causes pain. Enough 10-15 minutes for one session. The skin will then turn red, "burn".
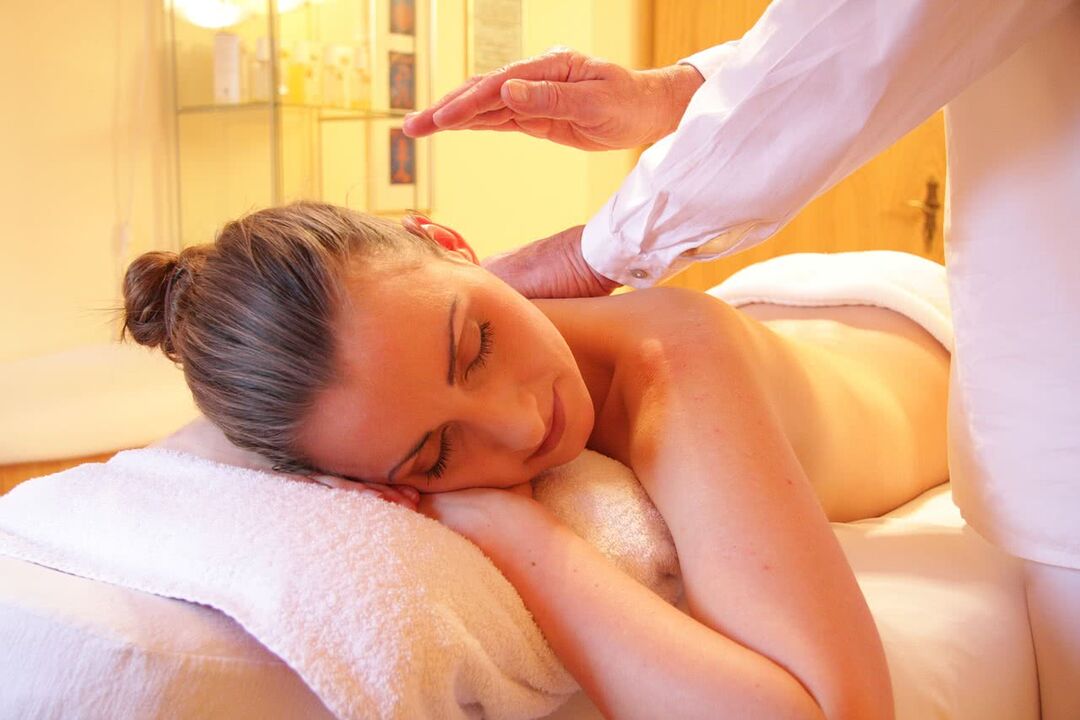

Classic massage. It consists of several steps, which include: stroking, kneading, vibrating, rubbing. It is recommended to perform the massage with an osteochondrosis cream or ointment: it can be recommended to you by the specialist present.
The duration of this massage should not exceed 20 minutes and the total course of treatment in this way should not include more than 11-13 sessions. As a preventive measure, it is also recommended to knead the neck, arms, shoulders, buttocks and even the legs.
Home treatments
Also, for the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis, there are alternative methods. For example, rubbing is very good, the basis of which can also be used when performing a massage. Lilac flowers, horseradish root, garlic, onions, potatoes, ficus are usually taken as a basis. Honey, vegetable oil, and sometimes cologne or alcohol are added. Everything is thoroughly mixed into a homogeneous mass and the damaged area is rubbed. For example, according to the following recipe, you can prepare a rub from ficus leaves:
- Ficus leaves in the amount of 6-8 are passed through a grater or cut into small pieces. Place in a container, where 2 bottles of triple cologne are poured. Mix. 2 weeks rubbing should be in a dark place. So you need to use it at least 2 times a day until heat appears on the skin.
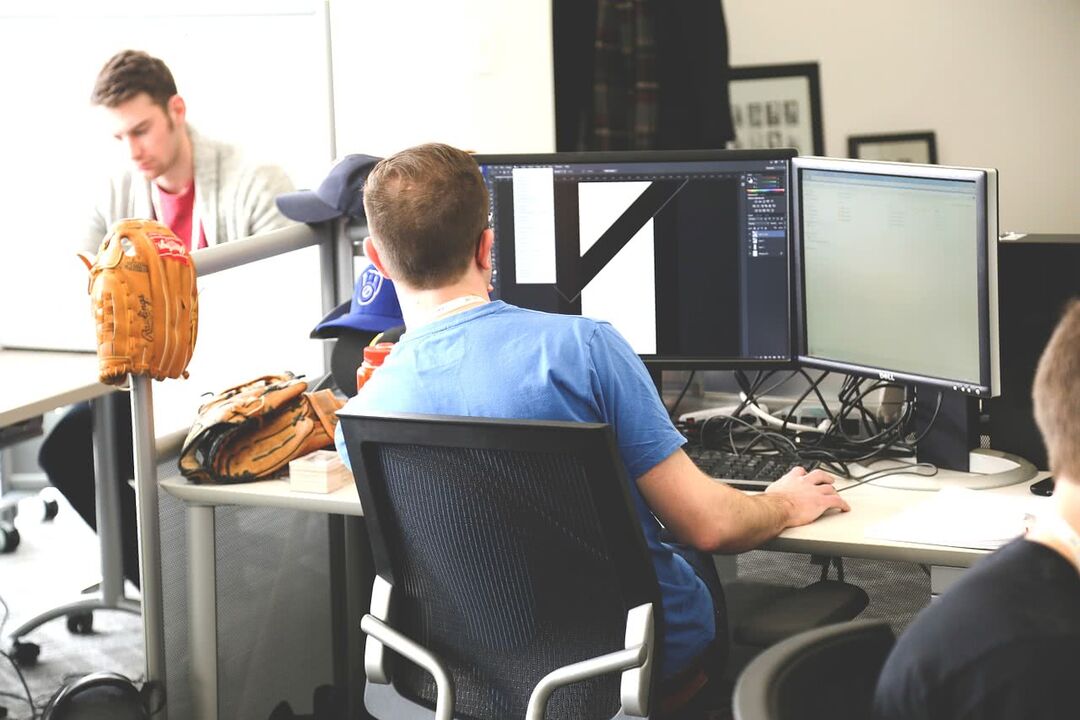

Working on a computer is a major cause of osteochondrosis. With a long stay at the computer, it is recommended to do exercises at least every two hours.
Doing computer activities every day without physical activity can lead to poor posture. This happens because a person performs static work for a long time, without letting the muscles and spine rest and without warming up or pausing. In the future, without correcting this problem, osteochondrosis of the thoracic region may develop.
To prevent this from happening, experts recommend performing the so-called office charging, designed specifically for those who work most of the time at the computer.
For example, the following exercises are very good:
- Arch your back by extending your arms upward, throwing your head back. Feel a pleasant heaviness in your back. Perform after every hour of computer work at least 3-4 times.
- Do circular rotations of the head. Look left and right, tilt your head forward and back.
- Raise your arms - to the sides - forward - to the sides. Repeat several times.
- Stay close to your workspace if you can and move from foot to foot.
Don't forget to change positions while working on the computer, so you will save your health, spine and posture for a long time!
Strengthening the back muscles with osteochondrosis
Strengthening the back muscles is a very important part in the treatment and prevention of osteochondrosis. To do this, it is enough to carry out physical activity: exercise, attend fitness classes or the gym. Choose the option that suits you best. For example, swimming strengthens muscles well, so you can not only have fun, but also improve your body.