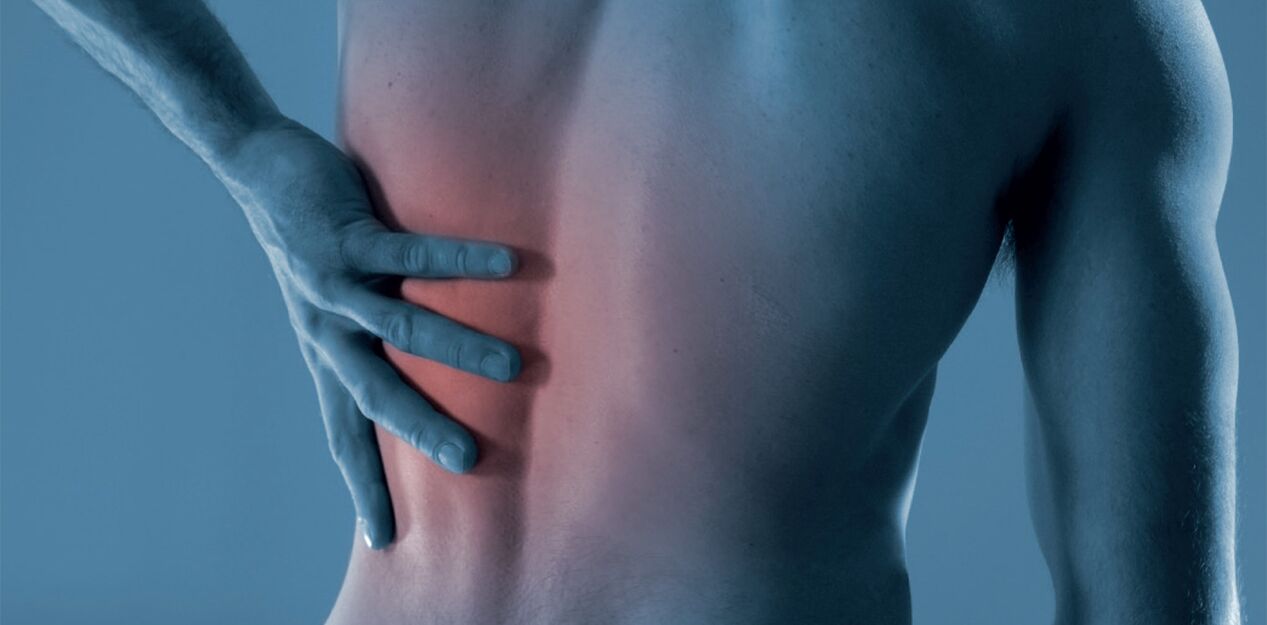
One of the most common pain syndromes is that associated with the lower back. According to some experts, pain in the lower back is a kind of punishment for humanity for walking upright, when the greatest load falls on the lumbar spine, which bears the main load of the mass of the human body. Physical inactivity, improper nutrition, obesity, stress also have a harmful effect. For many, back pain (lumbodynia) is so common that it becomes a part of everyday life. It can arise only once and disappear without a trace, or it can return again and again, causing considerable suffering.
Many of us at least once, but worried about pain in the lower back. Statistics say that this type of pain occurs in 90% of the population. The lower back can hurt with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, genitals, accompany menstruation in women. But most often, such pains are caused by osteochondrosis - degenerative-dystrophic changes of the spine. And among all the numerous painful syndromes of osteochondrosis, back pain occupies a leading position.
Lower back pain can be of a different nature: aching, which occurs after a long static load while sitting or while sleeping, or a sharp pull, which occurs with a sudden movement or is caught in an uncomfortable position. All are associated with pinching of the nerve roots, as well as spasm, swelling and irritation of the muscles and ligaments in the lumbar spine, which occur with osteochondrosis.
Causes of back pain
The lumbosacral spine is under maximum stress, and the intervertebral discs (the pads between the vertebrae) wear out much faster here. There are many causes of osteochondrosis in the lower back, but two main ones are: heavy and prolonged static load and an acute maximum load, which usually occurs when bending with heavy lifting. Here are some numbers. According to biomechanics, in the supine position, the intervertebral discs undergo a pressure of 50 kg, in an upright position - 100, in a sitting position with a straight back without support - 150 and sitting bent - 220.
Now calculate how much you sit in a day. . . And how much of this time hunched over, with a round back. . .
Other figures: when the body is tilted forward by only 20 ° without a load in the hands - 150 and with a load of only 10 kilograms (a couple of bags with shopping) - 200 kg, and if it tilts even lower, at an angle of 70 °, the load will increase to 300 kg. For example, according to biomechanical data, when a person lifts a weight of 50 kg in the forward leaning position, the load on the spine is 700 kg. Now answer the question yourself: do you lift heavy things? And from the floor? And with an inclination and rotation?
Back pain can be divided into primary and secondary pain. As you know, the spine is a series of vertebrae interconnected by elastic tissues - muscles and ligaments. They (in addition to bone tissue) contain nerve endings and can become a source of back pain.
The causes of primary back pain are due to the pathology of the spine - dystrophic and functional changes in the joints of the vertebrae, intervertebral discs, muscles, tendons, ligaments.
Secondary pain syndrome in the lower back is associated with traumatic injuries of the spine, tumors and infectious processes, diseases of the internal organs, osteoporosis and other pathologies. This is a kind of warning sign about malfunctions in the body. Particularly common causes of persistent low back pain are benign and malignant diseases of the pelvic organs (endometriosis, uterine fibroids, dysmenorrhea, lesions of the great vessels, kidneys, chronic prostatitis, some diseases of the nervous system).
There are 5 common causes of back pain:
Osteochondrosis (dorsopathy)- The most common source of pain in the lower back. The examination reveals degenerative diseases of the spine - osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis. The height of the intervertebral discs decreases, which leads to disturbances in the mechanical balance between the structures of the spine - hence the constant, quite tolerable, but periodically increasing pain in the lower back.
Muscle spasm.Have you experienced acute lower back pain while performing an intense and excessive physical activity that is unusual for you? The predisposing factor is a prolonged incorrect static position of the body (at the computer, squatting, bent in half during the summer cottage work). As a result, a muscle spasm develops, limiting the mobility of a certain part of the spine. Tense muscles become a source of pain, triggering a vicious cycle of low back pain - muscle spasm - pain. This condition can persist for a long time and causes many unpleasant minutes. Attention! For persistent low back pain, especially if it begins quickly and acutely, see a doctor to identify the underlying conditions and develop a modern and correct treatment.
Slipped disc, compressing the roots of the spinal cord, is particularly common in men over the age of 40. The first symptom of the disorder is low back in combination with a number of additional signs: pain along the root from the buttock to the foot when coughing, sneezing and laughing, difficulty in bending and extending the spine in the lumbar region (this is especially noticeable when wearing socks and shoes), increased unpleasant sensations when lifting a straight leg lying on the back. This back pain is often referred to as the outdated term sciatica or the colloquial word low back pain. Pain intensifies when standing and subsides in a horizontal position.
Spinal instabilityThis is a typical problem of middle-aged women. Manifested by back pain, aggravated by prolonged physical activity and standing position. At the same time, there is a feeling of fatigue and a desire to lie down. The disease is caused by damage to the disc or intervertebral joint and often occurs against a background of moderate obesity. It is difficult for such patients not to bend over, but to straighten up, to make "extra" movements.
Narrow spinal canal.The most common symptom is pain at rest combined with pain when walking. It spreads along the root from the buttocks to the feet, while it always hurts, even lying down or sitting, to the point that it is impossible to sit on the "sore" buttock. The syndrome of a narrow spinal canal is a consequence of degenerative changes, proliferation of the bone and joint structures of the spine, which leads to the violation of the roots of the spinal nerves.
Also, you have a real chance of experiencing back pain on your skin if:
- Overweight
- Do you like summer cottage jobs?
- You spend a lot of time driving a car or a computer
- Lead a predominantly sedentary (office worker) or standing lifestyle (vendors, waiters, road signs, surgeons)
- Overload in the gym or fitness club. Be very careful if you have recently started exercising.
- Do dynamic physical work with a sharp change in body position (especially if your specialty is associated with heavy physical activity)
Additional risk for women:
- You are pregnant or have recently given birth
- They have reached postmenopause, conducive to the development of osteoporosis
What to do for back pain:
And now, based on the above reasons, the same advice promised for those who want to reduce chronic lower back discomfort, as well as prevent the onset of back pain.
- Spend less time sitting. And if you still have to, then sit in the correct position.
- If you sit for long periods, be sure to take breaks every hour to perform more movements (stretches, pushups, simple walks, etc. ).
- Do not lift heavy objects. If you have to lift them, use the rules for lifting heavy objects.
- Contract your abdominal muscles as if closing tight pants. The abdominal muscles support the lumbar spine and by straining the abdomen, slightly relieve the load on the lower back.
- Exercise regularly for the spine and strengthen the muscle corset. Strong muscles will help you relieve excess stress on your lower back in any position. A flexible spine will help avoid pinching blood vessels and nerve endings.
- Find yourself a comfortable orthopedic mattress.
Also, for back pain, doctors usually recommend:
- A specialist can prescribe muscle relaxants to relieve muscle spasms, as well as diuretics and vascular drugs to reduce swelling of the nerve roots and improve blood circulation in the affected area.
- Relax for 2-5 days. As a rule, we are talking about bed rest on a hard, flat surface.
- Take pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They are available in tablets, solutions for injection and ointments.
- Wear a special bandage if necessary.
- Take a physical therapy course to consolidate the positive effect as your well-being improves. Physiotherapy procedures (magnetotherapy, electrophoresis, phonophoresis), as well as massage and physiotherapy exercises relieve muscle tension, improve blood circulation and stop the inflammatory process
- Resort to local therapy with ointments and gels containing analgesic, anti-inflammatory or warming components.
Recently, doctors have available double-acting agents: analgesics and muscle relaxants (muscle relaxants), which is very important in the treatment of pain syndrome in the pathology of the musculoskeletal system and in muscle spasm. These are drugs that have a triple effect: analgesic, muscle relaxant and neuroprotective (protecting nerve cells from damage). It is in fact a fundamentally new approach to treating back pain.
Whatever the cause of lower back pain, it is impossible to determine for yourself with certainty. If the back does not give rest either day or night, it is better to consult a specialist in a timely manner, who will tell you the tactics of treatment. All of these tips will help you prevent and reduce discomfort in the lumbar spine. But if you have acute pain in the lower back and sacrum, do not postpone the visit to the doctor. Give the final diagnosis to a specialist! Low back pain has a variety of causes, not necessarily associated with a pathology of the spine. In case of back pain and low back pain, it is recommended to undergo computed tomography (shows the state of the bone tissues of the spine) and magnetic resonance tomography (allows you to assess the condition of soft tissues). As a rule, most patients recover within 2-3 months, only a small number of patients with lumbodynia ailments reveal serious diseases.